Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
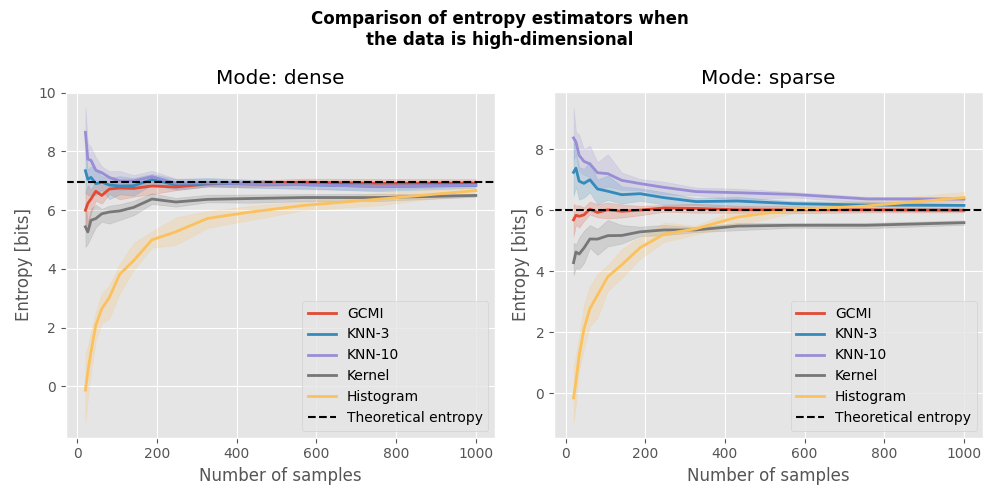
Comparison of entropy estimators with high-dimensional data#
In this example, we are going to compare estimators of entropy with high-dimensional data.
Simulate data sampled from a multivariate normal distribution.
Define estimators of entropy.
Compute the entropy for a varying number of samples.
See if the estimated entropy converge towards the theoretical value.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from hoi.core import get_entropy
plt.style.use("ggplot")
Definition of entropy estimators#
We are going to use the GCMI (Gaussian Copula Mutual Information), KNN (k Nearest Neighbor), a Gaussian kernel-based estimator and the histogram estimator.
# list of estimators to compare
metrics = {
"GCMI": get_entropy("gc", biascorrect=False),
"KNN-3": get_entropy("knn", k=3),
"KNN-10": get_entropy("knn", k=10),
"Kernel": get_entropy("kernel"),
"Histogram": get_entropy("histogram"),
}
# number of samples to simulate data
n_samples = np.geomspace(20, 1000, 15).astype(int)
# number of repetitions to estimate the percentile interval
n_repeat = 10
# plotting function
def plot(ent, ent_theoric, ax):
"""Plotting function."""
for n_m, metric_name in enumerate(ent.keys()):
# get the entropies
x = ent[metric_name]
# get the color
color = f"C{n_m}"
# estimate lower and upper bounds of the [5, 95]th percentile interval
x_low, x_high = np.percentile(x, [5, 95], axis=0)
# plot the MI as a function of the number of samples and interval
ax.plot(n_samples, x.mean(0), color=color, lw=2, label=metric_name)
ax.fill_between(n_samples, x_low, x_high, color=color, alpha=0.2)
# plot the theoretical value
ax.axhline(
ent_theoric, linestyle="--", color="k", label="Theoretical entropy"
)
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel("Number of samples")
ax.set_ylabel("Entropy [bits]")
Let variables \(X_1,X_2,...,X_n\) have a multivariate normal distribution \(\mathcal{N}(\vec{\mu}, \Sigma)\) the theoretical entropy in bits is defined by :
\[H(X) = \frac{1}{2} \times log_{2}({|\Sigma|}(2\pi e)^{n})\]
# function for creating the covariance matrix with differnt modes
def create_cov_matrix(n_dims, cov, mode="dense", k=None):
"""Create a covariance matrix."""
# variance 1 for each dim
cov_matrix = np.eye(n_dims)
if mode == "dense":
# all dimensions, but diagonal, with covariance cov
cov_matrix += cov
cov_matrix[np.diag_indices(n_dims)] = 1
elif mode == "sparse":
# only pairs x_i, x_(i+1) with i < k have covariance cov
k = k if k is not None else n_dims
for i in range(n_dims - 1):
if i < k:
cov_matrix[i, i + 1] = cov
cov_matrix[i + 1, i] = cov
return cov_matrix
def compute_true_entropy(cov_matrix):
"""Compute the true entropy (bits)."""
n_dims = cov_matrix.shape[0]
det_cov = np.linalg.det(cov_matrix)
return 0.5 * np.log2(det_cov * (2 * np.pi * np.e) ** n_dims)
# number of dimensions per variable
n_dims = 4
# mean
mu = [0.0] * n_dims
# covariance
covariance = 0.6
# modes for the covariance matrix:
# - dense: off diagonal elements have specified covariance
# - sparse: only pairs xi, x_(i+1) with i < k have specified covariance
modes = ["dense", "sparse"]
# number of pairs with specified covariance
k = n_dims
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
# compute entropy using various metrics
entropy = {k: np.zeros((n_repeat, len(n_samples))) for k in metrics.keys()}
for i, mode in enumerate(modes):
cov_matrix = create_cov_matrix(n_dims, covariance, mode=mode)
# define the theoretic entropy
ent_theoric = compute_true_entropy(cov_matrix)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
for n_s, s in enumerate(n_samples):
for n_r in range(n_repeat):
# generate samples from joint gaussian distribution
fx = np.random.multivariate_normal(mu, cov_matrix, s)
for metric, fcn in metrics.items():
# extract x and y
x = fx[:, :n_dims].T
y = fx[:, n_dims:].T
# compute entropy
entropy[metric][n_r, n_s] = fcn(x)
# plot the results
plot(entropy, ent_theoric, ax)
ax.title.set_text(f"Mode: {mode}")
fig.suptitle(
"Comparison of entropy estimators when\nthe data is high-dimensional",
fontweight="bold",
)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 22.951 seconds)