hoi.metrics.Oinfo#
- class hoi.metrics.Oinfo(x, y=None, multiplets=None, verbose=None)[source]#
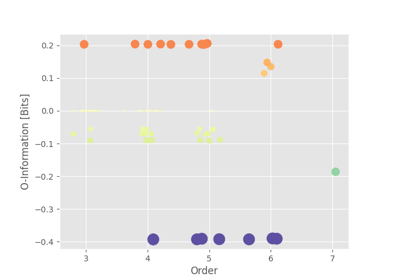
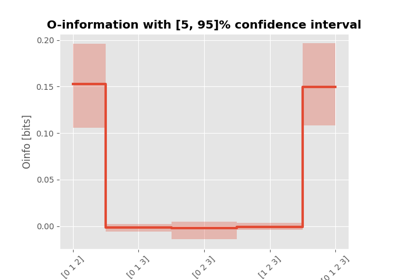
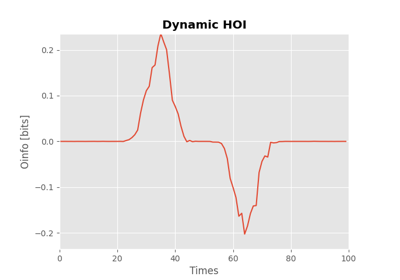
O-information.
The O-information is defined as the difference between the total correlation (TC) minus the dual total correlation (DTC):
\[\begin{split}\Omega(X^{n}) &= TC(X^{n}) - DTC(X^{n}) \\ &= (n - 2)H(X^{n}) + \sum_{j=1}^{n} [H(X_{j}) - H( X_{-j}^{n})]\end{split}\]Warning
\(\Omega(X^{n}) > 0 \Rightarrow Redundancy\)
\(\Omega(X^{n}) < 0 \Rightarrow Synergy\)
- Parameters:
- xarray_like
Standard NumPy arrays of shape (n_samples, n_features) or (n_samples, n_features, n_variables)
- yarray_like
The feature of shape (n_samples,) for estimating task-related O-info
- multipletslist | None
List of multiplets to compute. Should be a list of multiplets, for example [(0, 1, 2), (2, 7, 8, 9)]. By default, all multiplets are going to be computed.
- Attributes:
entropiesEntropies of shape (n_mult,)
multipletsIndices of the multiplets of shape (n_mult, maxsize).
orderOrder of each multiplet of shape (n_mult,).
undersamplingUnder-sampling threshold.
Methods
compute_entropies([method, minsize, ...])Compute entropies for all multiplets.
fit([minsize, maxsize, method, samples])Compute the O-information.
get_combinations(minsize[, maxsize, astype])Get combinations of features.
References
Rosas et al., 2019 [24]
- __iter__()#
Iteration over orders.
- compute_entropies(method='gc', minsize=1, maxsize=None, samples=None, **kwargs)#
Compute entropies for all multiplets.
- Parameters:
- method{‘gc’, ‘binning’, ‘knn’, ‘kernel}
Name of the method to compute entropy. Use either :
‘gc’: gaussian copula entropy [default]. See
hoi.core.entropy_gc()‘binning’: binning-based estimator of entropy. Note that to use this estimator, the data have be to discretized. See
hoi.core.entropy_bin()‘knn’: k-nearest neighbor estimator. See
hoi.core.entropy_knn()‘kernel’: kernel-based estimator of entropy see
hoi.core.entropy_kernel()
- samplesnp.ndarray
List of samples to use to compute HOI. If None, all samples are going to be used.
- minsizeint, optional
Minimum size of the multiplets. Default is 1.
- maxsizeint, optional
Maximum size of the multiplets. Default is None.
- kwargsdict, optional
Additional arguments to pass to the entropy function.
- Returns:
- h_xarray_like
Entropies of shape (n_mult, n_variables)
- h_idxarray_like
Indices of the multiplets of shape (n_mult, maxsize)
- orderarray_like
Order of each multiplet of shape (n_mult,)
- property entropies#
Entropies of shape (n_mult,)
- fit(minsize=2, maxsize=None, method='gc', samples=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Compute the O-information.
- Parameters:
- minsize, maxsizeint | 2, None
Minimum and maximum size of the multiplets
- method{‘gc’, ‘binning’, ‘knn’, ‘kernel’, callable}
Name of the method to compute entropy. Use either :
‘gc’: gaussian copula entropy [default]. See
hoi.core.entropy_gc()‘gauss’: gaussian entropy. See
hoi.core.entropy_gauss()‘binning’: binning-based estimator of entropy. Note that to use this estimator, the data have be to discretized. See
hoi.core.entropy_bin()‘knn’: k-nearest neighbor estimator. See
hoi.core.entropy_knn()‘kernel’: kernel-based estimator of entropy see
hoi.core.entropy_kernel()A custom entropy estimator can be provided. It should be a callable function written with Jax taking a single 2D input of shape (n_features, n_samples) and returning a float.
- samplesnp.ndarray
List of samples to use to compute HOI. If None, all samples are going to be used.
- kwargsdict | {}
Additional arguments are sent to each entropy function
- Returns:
- hoiarray_like
The NumPy array containing values of higher-order interactions of shape (n_multiplets, n_variables)
- get_combinations(minsize, maxsize=None, astype='jax')#
Get combinations of features.
- Parameters:
- minsizeint
Minimum size of the multiplets
- maxsizeint | None
Maximum size of the multiplets. If None, minsize is used.
- astype{‘jax’, ‘numpy’, ‘iterator’}
Specify the output type. Use either ‘jax’ get the data as a jax array [default], ‘numpy’ for NumPy array or ‘iterator’.
- Returns:
- combinationsarray_like
Combinations of features.
- property multiplets#
Indices of the multiplets of shape (n_mult, maxsize).
By convention, we used -1 to indicate that a feature has been ignored.
- property order#
Order of each multiplet of shape (n_mult,).
- property undersampling#
Under-sampling threshold.
Examples using hoi.metrics.Oinfo#
O-information and its derivatives for network behavior and encoding