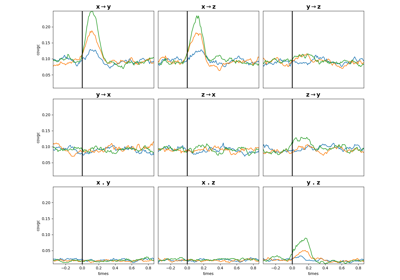
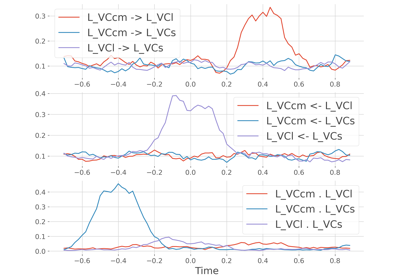
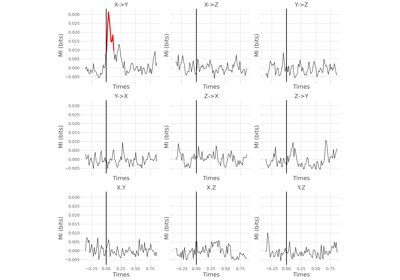
frites.conn.conn_covgc#
- frites.conn.conn_covgc(data, dt, lag, t0, step=1, roi=None, times=None, method='gc', conditional=False, norm=False, gcrn=False, n_jobs=-1, verbose=None, **kw_links)[source]#
Single-trial covariance-based Granger Causality for gaussian variables.
This function computes the (conditional) covariance-based Granger Causality (covgc) for each trial.
Note
Total Granger interdependence
TGI = gc.sum(axis=-1) = gc(x->y) + gc(y->x) + gc(x.y)
TGI = Hycy + Hxcx - Hxxcyy
Relations between Mutual Informarion and conditional entropies
This quantity can be defined as the Increment of Total Interdependence and it can be calculated from the different of two mutual informations as follows
\[\begin{split}Ixxyy &= I(X_{i+1}, X_{i}|Y_{i+1}, Y_{i}) \\ &= H(X_{i+1}) + H(Y_{i+1}) - H(X_{i+1},Y_{i+1}) \\ &= log(det_{xi1}) + log(det_{yi1}) - log(det_{xyi1}) \\ Ixy &= I(X_{i}|Y_{i}) \\ &= H(X_{i}) + H(Y_{i}) - H(X_{i}, Y_{i}) \\ &= log(det_{xi}) + log(det_{yi}) - log(det_{yxi}) \\ ITI &= Ixxyy - Ixy\end{split}\]- Parameters:
- datanumpy:array_like
Electrophysiological data. Several input types are supported :
Standard NumPy arrays of shape (n_epochs, n_roi, n_times)
mne.Epochs
xarray.DataArray of shape (n_epochs, n_roi, n_times)
- dt
python:int Duration of the time window for covariance correlation in samples
- lag
python:int Number of samples for the lag within each trial
- t0numpy:array_like
Array of zero time in samples of length (n_window,)
- step
python:int| 1 Number of samples stepping in the past for the lag within each trial
- timesnumpy:array_like |
python:None Time vector array of shape (n_times,). If the input is an xarray, the name of the time dimension can be provided
- roinumpy:array_like |
python:None ROI names of a single subject. If the input is an xarray, the name of the ROI dimension can be provided
- method{‘gauss’, ‘gc’}
Method for the estimation of the covgc. Use either ‘gauss’ which assumes that the time-points are normally distributed or ‘gc’ in order to use the gaussian-copula.
- conditionalbool |
python:False If True, the conditional Granger Causality is computed i.e the past is also conditioned by the past of other sources.
- normbool |
python:False If True, the normalised Granger Causality is computed See [6].
- n_jobs
python:int| -1 Number of jobs to use for parallel computing (use -1 to use all jobs). The parallel loop is set at the pair level.
- kw_links
python:dict| {} Additional arguments for selecting links to compute are passed to the function
frites.conn.conn_links()
- Returns:
- gcnumpy:array_like
Granger Causality arranged as (n_epochs, n_pairs, n_windows, 3) where the last dimension means :
0 : pairs[:, 0] -> pairs[:, 1] (x->y)
1 : pairs[:, 1] -> pairs[:, 0] (y->x)
2 : instantaneous (x.y)
See also
References
Brovelli et al., 2015 [1]
Examples using frites.conn.conn_covgc#
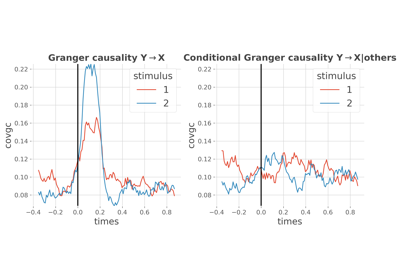
AR : conditional covariance based Granger Causality
Statistical analysis of a stimulus-specific network