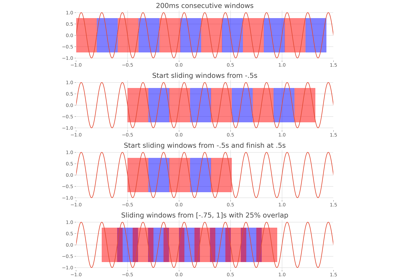
frites.conn.define_windows#
- frites.conn.define_windows(times, windows=None, slwin_len=None, slwin_start=None, slwin_stop=None, slwin_step=None, sfreq=None, verbose=None)[source]#
Define temporal windows.
This function can be used to either manually define temporal windows either automatic sliding windows. Note that every input parameters should be in the time domain (e.g seconds or milliseconds).
- Parameters:
- timesnumpy:array_like
Time vector
- windowsnumpy:array_like |
python:None Manual windows (e.g (.1, .2) or [(.1, .2), (.4, .5)]).
- slwin_len
python:float|python:None Length of each sliding (e.g .2 produces 200ms window length).
- slwin_start
python:float|python:None Time point for starting sliding windows (e.g 0.1). If None, sliding windows will start from the first time point.
- slwin_stop
python:float|python:None Time point for ending sliding windows (e.g 1.5). If None, sliding windows will finish at the last time point.
- slwin_step
python:float|python:None Temporal step between each temporal window (e.g .1 means that each consecutive windows are going to be separated by 100ms). This parameter can be used to define either overlapping or non-overlapping windows. If None, slwin_step is going to be set to slwin_step in order to produce consecutive non-overlapping windows.
- sfreq
python:float|python:None The sampling frequency
- Returns:
- win_samplenumpy:array_like
Array of shape (n_windows, 2) of temporal indexes defining where each window (start, finish)
- mean_timenumpy:array_like
Mean time vector inside each defined window of shape (n_windows,)
See also
Examples using frites.conn.define_windows#
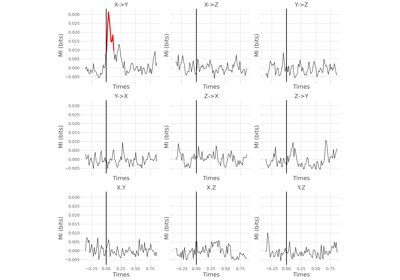
Statistical analysis of a stimulus-specific network