Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Estimator comparison#
This example compares implemented estimators for continuous variables.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from frites.estimator import (GCMIEstimator, BinMIEstimator, CorrEstimator,
DcorrEstimator)
from frites import set_mpl_style
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
set_mpl_style()
Functions for data simulation#
This first part contains functions used for simulating data.
def gen_mv_normal(n, cov):
"""Generate multi-variate normals."""
sd = np.array([[1, cov], [cov, 1]])
mean = np.array([0, 0])
xy = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, sd, size=n)
xy += np.random.rand(*xy.shape) / 1000.
x = xy[:, 0]
y = xy[:, 1]
return x, y
def rotate(xy, t):
"""Distribution rotation."""
rot = np.array([[np.cos(t), np.sin(t)], [-np.sin(t), np.cos(t)]]).T
return np.dot(xy, rot)
def generate_data(n, idx):
"""Generate simulated data."""
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, n)
mv_covs = [1.0, 0.8, 0.4, 0.0, -0.4, -0.8, -1.0]
if idx in np.arange(7): # multi-variate
x, y = gen_mv_normal(n, mv_covs[idx])
name = f'Multivariate (cov={mv_covs[idx]})'
xlim = ylim = [-5, 5]
elif idx == 7: # curvy
r = (np.random.random(n) * 2) - 1
y = 4.0 * (x ** 2 - 0.5) ** 2 + (r / 3)
name = 'Curvy'
xlim, ylim = [-1, 1], [-1 / 3.0, 1 + (1 / 3.0)]
if idx == 8: # rotated uniform
y = np.random.random(n) * 2 - 1
xy = rotate(np.c_[x, y], -np.pi / 8.0)
lim = np.sqrt(2 + np.sqrt(2)) / np.sqrt(2)
x, y = xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1]
name = 'Rotated uniform (1)'
xlim = ylim = [-lim, lim]
if idx == 9: # rotated uniform
y = np.random.random(n) * 2 - 1
xy = rotate(np.c_[x, y], -np.pi / 4.0)
lim = np.sqrt(2)
x, y = xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1]
name = 'Rotated uniform (2)'
xlim = ylim = [-lim, lim]
if idx == 10: # smile
r = (np.random.random(n) * 2) - 1
y = 2 * (x ** 2) + r
xlim, ylim = [-1, 1], [-1, 3]
name = 'Smile'
if idx == 11: # mirrored smile
r = np.random.random(n) / 2.0
y = x ** 2 + r
flipidx = np.random.permutation(len(y))[:int(n / 2)]
y[flipidx] = -y[flipidx]
name = 'Mirrored smile'
xlim, ylim = [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]
if idx == 12: # circle
r = np.random.normal(0, 1 / 8.0, n)
y = np.cos(x * np.pi) + r
r = np.random.normal(0, 1 / 8.0, n)
x = np.sin(x * np.pi) + r
name = 'Circle'
xlim, ylim = [-1.5, 1.5], [-1.5, 1.5]
if idx == 13: # 4 clusters
sd = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]])
xy1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3, 3], sd, int(n / 4))
xy2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([-3, 3], sd, int(n / 4))
xy3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([-3, -3], sd, int(n / 4))
xy4 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3, -3], sd, int(n / 4))
xy = np.r_[xy1, xy2, xy3, xy4]
x, y = xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1]
name = '4 clusters'
xlim = ylim = [-7, 7]
return name, x, y, xlim, ylim
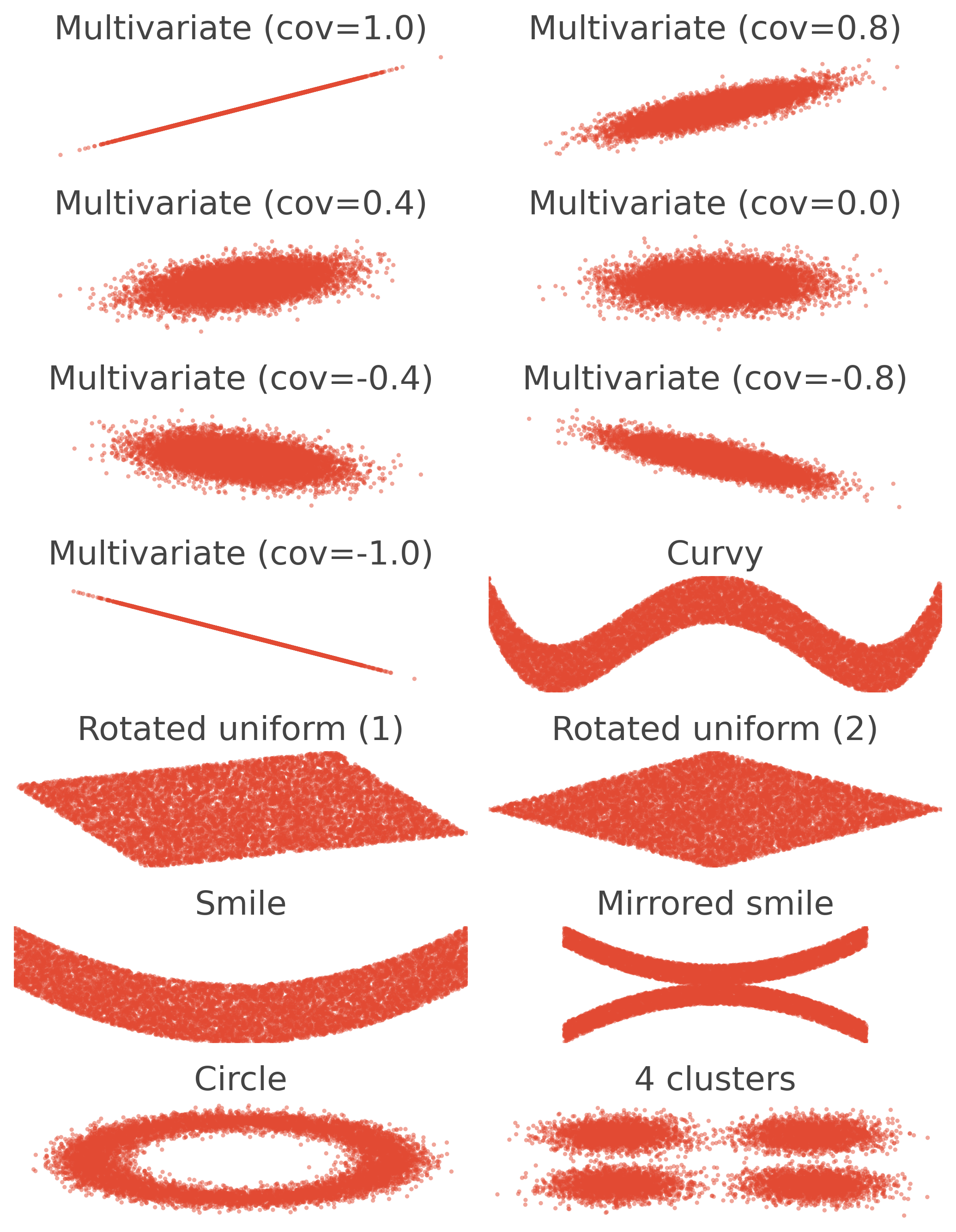
Plot the simulated data#
In this section, we plot several scenarios of relation between a variable x and a variable y. The scenarios involve linear, non-linear, monotonic and non-monotonic relations.
# number of points
n = 10000
# plot the data
fig_data = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 9))
for i in range(14):
name, x, y, xlim, ylim = generate_data(n, i)
plt.subplot(7, 2, i + 1)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.scatter(x, y, s=5, edgecolors='none', alpha=.5)
plt.xlim(xlim)
plt.ylim(ylim)
plt.title(name)
ax.axis(False)
fig_data.tight_layout()
plt.show()